Ai Mediq announces it’s participation in largest professional event in MENA region – Arab Health 2020. The event will…


Ai Mediq announces it’s participation in largest professional event in MENA region – Arab Health 2020. The event will…
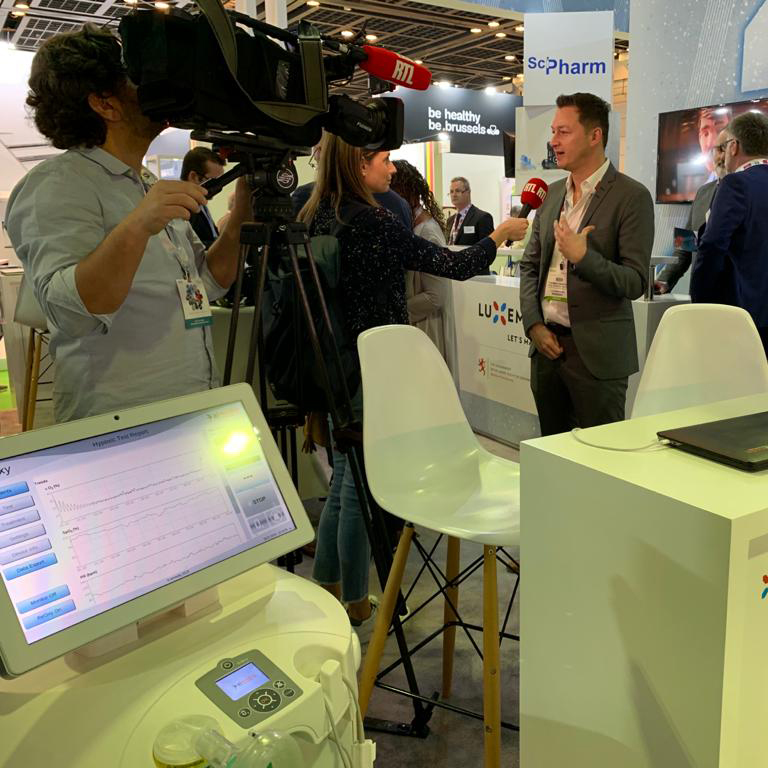

Official Business Mission of Grand Duchy of Luxembourg has visited Arab Health 2020 trade-show yesterday, on 28th of January.
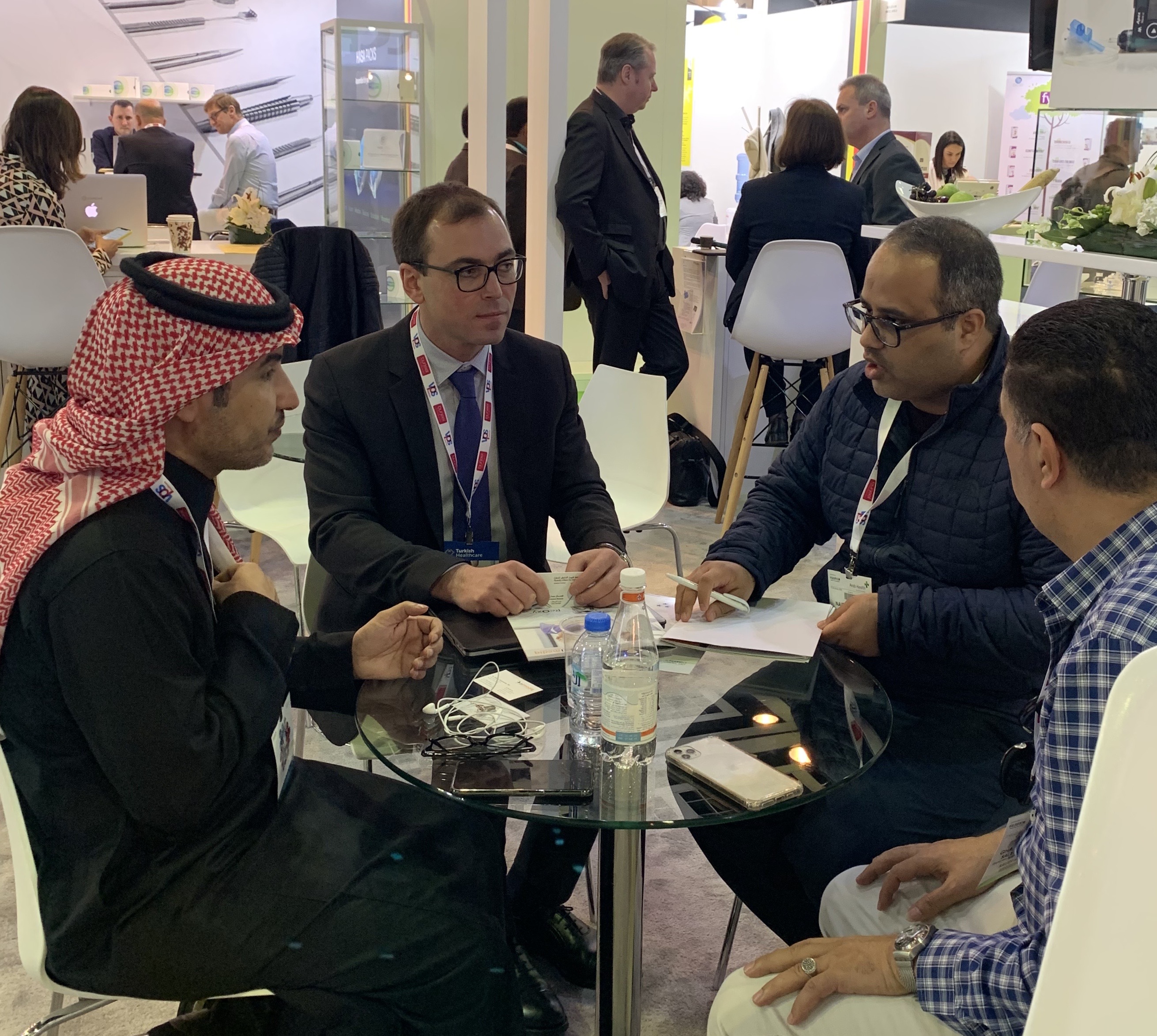

Yesterday, on 30th of January 2020 was the final day both of one of the largest medical trade-shows Arab Health and Official Mission of Grand Duchy of Luxembourg to the United Arab Emirates. Ai Mediq was thrilled to take part in both of these remarkable events with very promising outcomes.
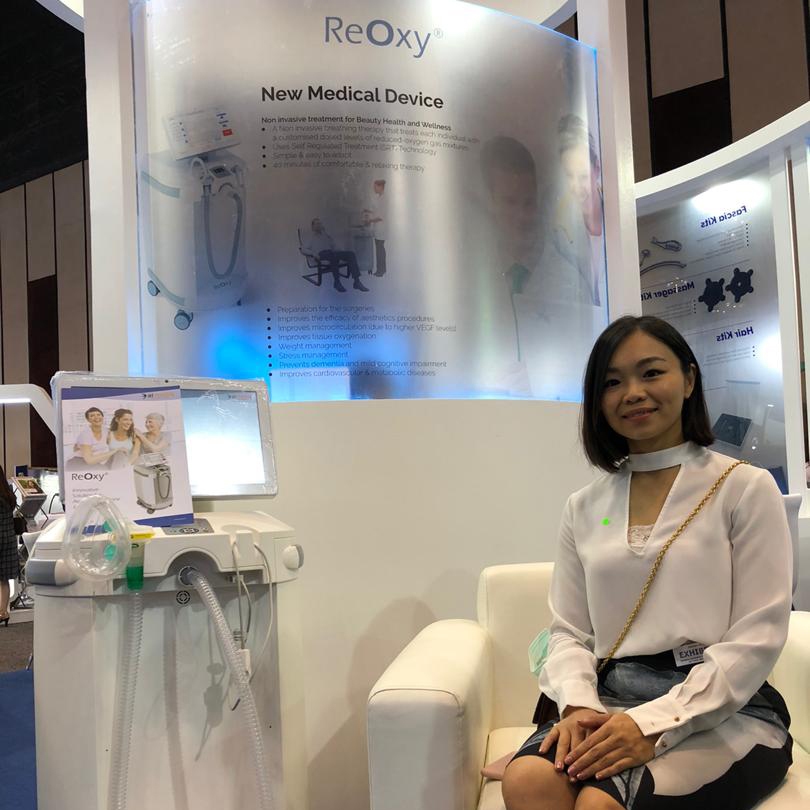

This February our leading instrument for delivering Interval Hypoxic Hyperoxic Therapy — ReOxy is presented to the attention of the general public in Bangkok, Thailand during the 24th Regional Conference of Dermatology taking place from 25th till 28th of February.
Currently, all efforts are focused on patients with acute diseases. All hospitals are crowded with severe patients with COVID-19 who need emergency care to save their lives.
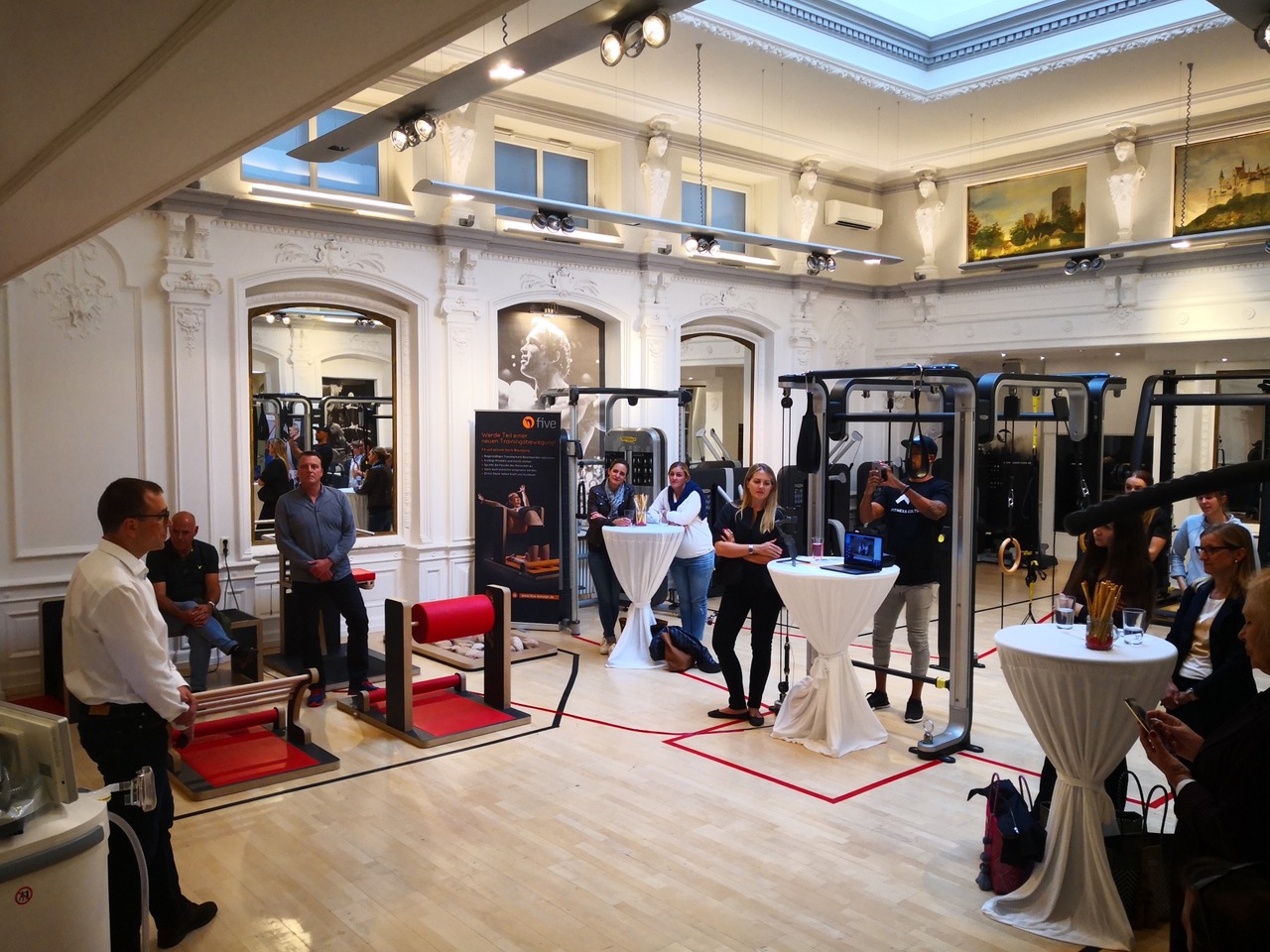

Presentation of the Intermittent Hypoxic Training Method in one of the well-known Liliane Goschy-FRITZ Institute in Baden-Baden, Germany on the 15th if July 2020.

IntroductionIntermittent hypoxic–hyperoxic training (IHHT) may complement a multimodal training intervention (MTI) for improving cognitive function and exercise tolerance in geriatric patients. MethodsThirty-four patients (64–92 years) participated in this randomized controlled trial. Before and after the 5- to 7-week intervention period (MTI 1 IHHT vs. MTI 1 ambient air), cognitive func- tion was assessed by the Dementia-Detection Test (DemTect) and the Sunderland Clock-Drawing Test (CDT), and…

SummaryOvertraining syndrome (OTS) is a major concern among endurance athletes and is a leading cause in preventing them to perform for long periods. Intermittent exposure to hypoxia has been shown to be an effective way of improving perfor- mance without exercising. Aim of this pilot study was to evaluate intermittent hypoxia–hyperoxia training combined with light exercise as an intervention to facilitate athletes with OTS to…

Background: Repeated exposure to intermittent normobaric hypoxia improves exercise tolerance in cardiac patients. Little is known on the effects of intermittent normobaric hypoxia-hyperoxia exposure in coronary artery disease (CAD) patients (New York Heart Association II-III). Hypothesis: IHHT improves exercise tolerance, cardiometabolic profile, and quality of life in CAD patients. Methods: The study design was a nonrandomized, controlled, before-and-after trial. Forty-six CAD patients volunteered to take…

Aim: To compare a program based on intermittent hypoxia-hyperoxia training (IHHT) consisting of breathing hypoxic-hyperoxic gas mixtures while resting to a standard exercise-based rehabilitation program with respect to cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) in older, comorbid cardiac outpatients. Materials and methods: Thirty-two cardiac patients with comorbidities were randomly allocated to IHHT and control (CTRL) groups. IHHT completed a 5-week program of exposure to hypoxia-hyperoxia while resting, CTRL…