Unveiling the Benefits of Controlled Hypoxia
Hypoxia, traditionally viewed as a negative factor for the body, possesses remarkable potential when precisely harnessed. In this article, we delve into the positive effects of intermittent hypoxia and explore the underlying mechanisms driving these benefits.
Controlled Hypoxia and the Principle of Hormesis
Hypoxia is defined as a state where body tissues, organs, or cells lack sufficient oxygen supplies. It arises from various factors preventing effective oxygen distribution. Often associated with diseases, numerous scientific studies challenge its negative connotation, showcasing its ability to enhance performance, regulate metabolism, relieve pain, and combat cardiovascular and metabolic disorders when administered in controlled doses.
Based on the scientific evidence, novel hypoxia administration techniques, termed ‘hypoxic conditioning,’ have emerged. These methods deliver controlled intermittent hypoxia and have been tested in clinical settings, demonstrating promising benefits when cautiously applied.
The key lies in control: while acute or prolonged hypoxia can be harmful, evidence suggests that controlled and low doses trigger positive adaptations. This dual response aligns with the principle of “hormesis,” wherein exposure to low doses of a typically toxic agent elicits a beneficial or stimulatory effect. In that case, controlled exposure to hypoxia increases cellular resilience and resistance to conditions provoked by it.
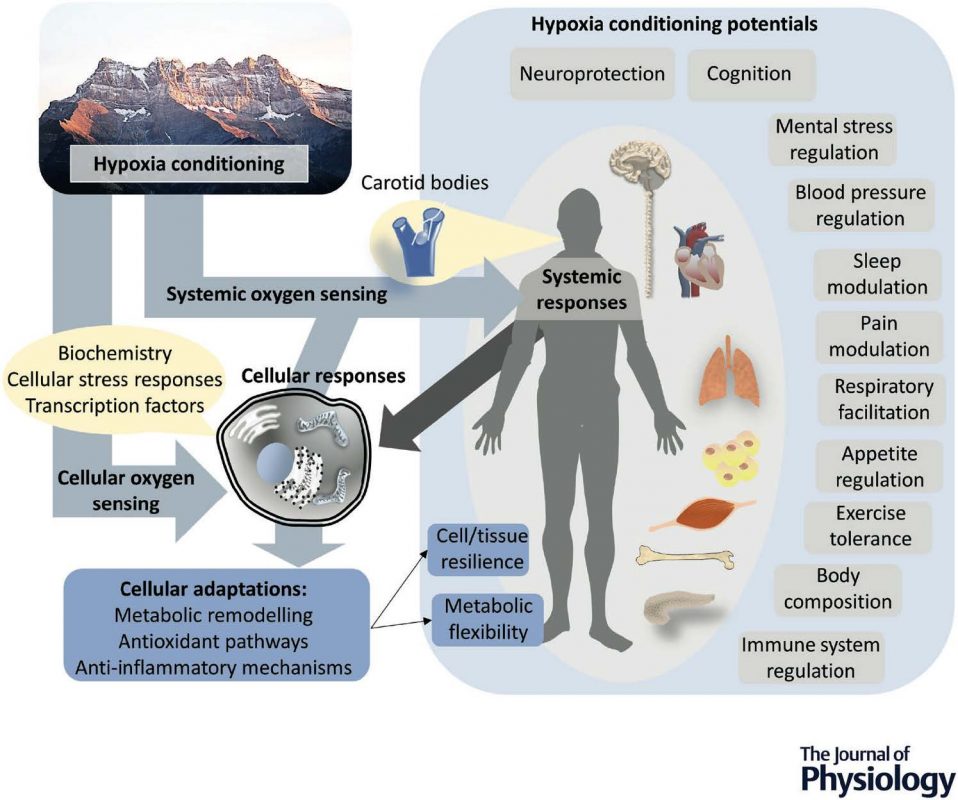
Adaptive response to hypoxia improve cellular resilience and functions. Source: Burtscher et all. The journal of physiology, 2023. PMID: 37860950
The hypoxia response occurs at different levels
At the molecular level, hypoxia triggers three key transcription factors crucial in mediating adaptation:
- HIFs regulating oxygen supply (erythropoiesis, vascular remodeling) and ATP production (glucose transport and glycolysis);
- Nrf2 managing antioxidant defenses;
- NFkB modulating the inflammatory response.
It has been shown that some cellular pathways (HIF, AMPK, mTOR, DNA damage, unfolded protein response) exhibit hypoxia dose-dependent responses and contribute to hypoxia adaptation.
As a starting point for the cellular hypoxic response, those molecular mechanisms act as sensors and drive numerous reactions to hypoxia at cellular and systemic levels.
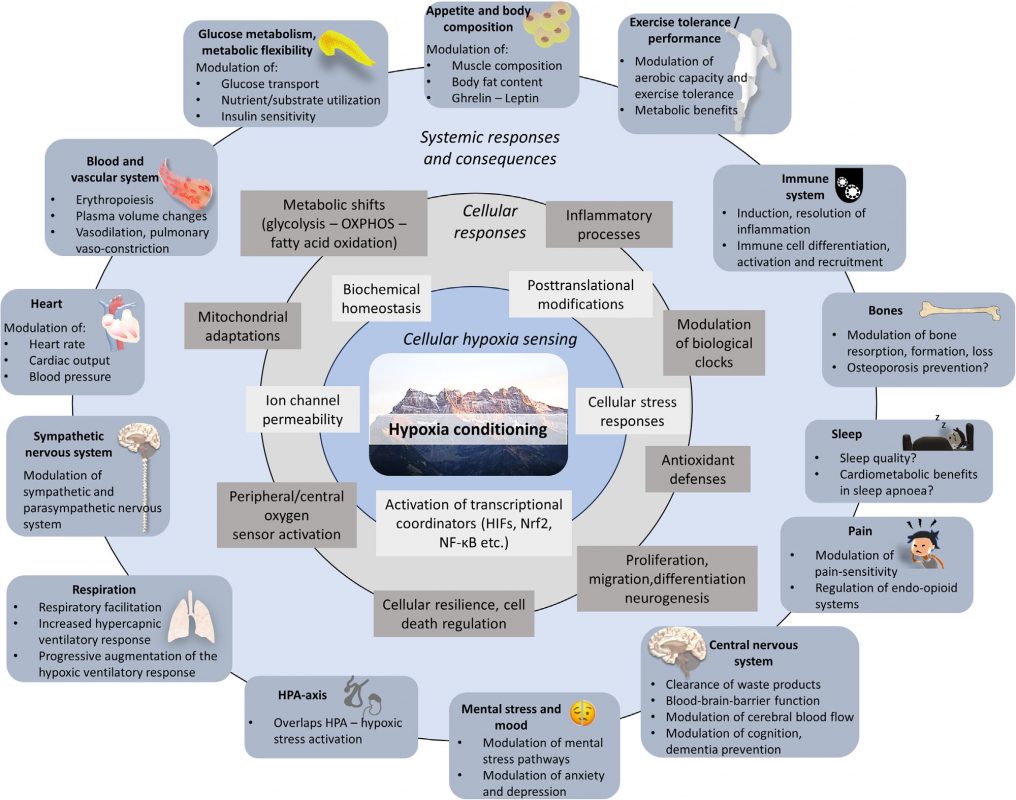
Overview of mechanisms and benefits potentially triggered by hypoxia conditioning. Source: Burtscher et all. The journal of physiology, 2023. PMID: 37860950
ReOxy®: addressing the beneficial effects
Considering the importance of dosage, clinically validated protocols and medically compliant devices are crucial for patient safety. ReOxy® has been developed to tackle those matters and optimize the beneficial effects for patients. Presently, among the number of possible positive effects to address, ReOxy® evaluation is focused on several areas:
| Evaluation Type | Area of Study | Benefits |
| Clinically Proven | Cardiac Rehabilitation | – Enhanced tolerance to physical load
– Improved tolerance to acute ischemic episodes – Reduced damaging effect of acute ischemic events |
| Ongoing Clinical Evaluation | Long COVID | – Improved physical capacity
– Enhanced quality of life – Reduced Fatigue – Improved subjective perceived health |
| Neuro-rehabilitation | – Increased global cognitive function in geriatric patients | |
| Prospective Evaluation | Pulmonary Function | – Enhanced respiratory capacity and microcirculation
– Improved gas exchange – Reduced respiratory discomfort (shortness of breath, asthma attacks, coughing) – Improved physical performance |
| Metabolism | – Improves weight loss
– Lowers cholesterol and glucose levels – Improves activities for fat-burning enzymes – Potential treatment for metabolic diseases (diabetes, obesity) |
|
| Traumatology/Orthopedics | – Decrease the length of post-injury recovery during sports rehabilitation
– Enhance walking recovery in persons with incomplete spinal cord injury |
Source: ReOxy clinical evidences
Conclusion
Understanding and harnessing controlled hypoxia through devices like ReOxy® opens doors to transformative medical interventions. Our exploration of hypoxia’s positive effects reshapes conventional approaches, offering promising prospects across diverse medical domains.